BlockChain technology is the last KETTL presented because differentiated origins and potential impact. As already explained, IA, Robotics, IoT, Enhanced Reality and Autonomous Vehicles integrate and leverage each other, and have been systematically applied in manufacturing to later pour into Transport and Logistics. Sectors. On the other side BlockChain is an independent technology that emerged in 2009 with the limited function to protect cryptocurrencies and that has surprisingly evolved to be applied to any kind of transaction in any industry. BlockChain also diverges from most other KETTLs as it can be considered a disruptive technology with the potential to severely alter all processes related to digital transactions and their contract enforcement and management.
Therefore, we suggest to look at BlockChain as much more that facilitating bitcoins, rather as a fast-advancing technology near to be able to offer enormous improvement in security, transparency, quality, reliability in any kind of transactions. BlockChain brings this increased security and transparency just when is more needed, now that other KETTLs are making possible and inevitable more complex transactions and increased cooperation.
BLOCKCHAIN DESCRIPTION AND COMPONENTS
BlockChain technology attracts wide interest as a security alternative way to conduct complex, multi-sided transactions and information sharing without the need for a third-party intervention and guarantee. It was born in 2009 as a way to protect cryptocurrencies and allows to conduct any type of transaction in an immutable, reliable, accessible, secure and traceable way.
Distributed Ledger
BlockChain is based on Distributed Ledger Technology (D.L.T.) with online, public and decentralized ledgers which record and share all transactions carried out. Unlike traditional databases, this record is synchronized between all and each of the parties participating. Everything is simultaneously registered in each of the ledgers own by each party, so that all participants share the same information.
Cryptography and Peer-to Peer Network Protocols
BlockChain also offers a suitable balance between security and transparency and provides a fundamental characteristic to fight against fraud: it allows adding new information, but makes it impossible to undo or rewrite the one already registered. That is achieved by cryptographic keys that serve as digital identities among transacting partners, plus a distributed peer-to-peer network managed by a network protocol agreed by all parties and that directly manages each of the decentralized ledgers without possibility of alteration.
Smart Contracts
The so called Smart Contracts are software programs that collect the terms of a contract between the parties and that are stored in the BlockChain, with the peculiarity that they are self-executing when a series of conditions specified in the contract itself are met. In this way intermediaries are avoided, reducing costs and bureaucratic delays and providing greater visibility and confidence. Additionally, this is an Open Source technology and allows all parties to a transaction or workflow to see the same information at the same time, including regulators.
BLOCKCHAIN ADOPTION
Considering its benefits and relative technological simplicity BlockChain technology still has not jumped into a board use. Analysis coincide to point out its cryptocurrency origins that generates distrust among enterprises plus the very important fact that BlockChain vendor’s Platforms do not offer compatible standards and enterprises are adamant of becoming strategically dependent on a single vendor
BlockChain presents a clear case of Network Economies, when a linear increase of users triggers and exponential growth of value. Therefore, competing and incompatible standards exponentially reduces the value of using them as incompatibility place users in separated networks or simply deters them from using any of them. For this same reason once standards and compatibility are stablishing and enormous growth in use and value is expected.
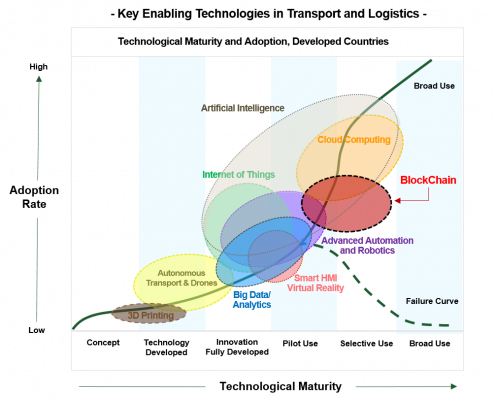
CETMO Analysis, adapted from McKinsey & Company (3)
As expected major investments by big players have recently being done, IBM, Microsoft and Accenture already counted for 68% of BlockChain supplier sales by 2018 (1) and in 2019 Amazon, Microsoft and IBM, the three major Cloud Service providers, had already included BlockChain services within their Could Computing Platforms. BlockChain services through the cloud is a potential market of $420.5 billion expected to reach USD 982.8 billion by 2025 (2), and interestingly its major growth is happening in Asian countries.
BLOCKCHAIN USES AND EFFECTS
A downright effect of BlockChain adoption is the reduction of transaction costs as financial institutions and other third parties that stablish credibility are not required plus the elimination of payment delays. Also for developing countries when offered in broader Digital Platforms provides a contractual, transactional and financial digital infrastructure without requiring a previous banking or financial institutions base thus facilitating all kind of economic transactions and economic growth.
Already describing other KETTLs we have presented that many favor the creation of production, transaction, and consumption, collaboration and integration among agents to the point of creating new business ecosystems. BlockChain with its inherent transparency acts as the glue of those emerging ecosystems. Its applications for economic development are straightforward. Also administrations, in Australia, EU, Korea and USA are exploring applications in identity management, data portability and voting systems.
References:
- Bloomberg, Kharif, BlockChain once seen as a corporate cure-all suffers slowdown, 2018. link
- Business Wire, BlockChain-as-a-Service (BaaS) Market Outlook to 2025: Growth, Trends, Companies, 2020. link
- McKinsey & Company. Ashutosh, Hastings, Murnane, Neuhaus, Automation in Logistics: Big Opportunity, Bigger Uncertainty, 2019. link
Blockchain enables a more exhaustive control of all stages of transport among different agents which gives total security and confidence between the different agents involved in the logistics chain. This allows for broad alliances among companies and an increase of the quality of services. Regarding Passenger Transport, BlockChain facilitates a more open market, decentralized, multimodal and multi-provider mobility that increases user’s benefits. Also opens the door to new ways of conducting business and facilitate transaction in situations that were not possible before.
Freight Transport
Enhanced Transparency and Cooperation: with BlockChain technology information throughout the value chain is transmitted and shared among all actors faster and in a 100% reliable and impossible to manipulate way. Errors along the supply chain can be detected more clearly and bad practices or lack of quality become transparent to the customer and to the provider, and can be addressed.
This increase in transparency among value chain actors and its derived trust will allow for enhanced planning and offering of integrated services and networked services, also multimodal. and accountable to agents in a dynamic way
More Accurate Demand Forecasts as information between suppliers and producer’s flows in real time, and is more fluid and Connected. Thus, transport companies that, in commercial, legal and administrative terms, are totally separated from each other and their customers in practice can analyze and plan as if their activity was Connected and act as a single company department.
Faster and Audited Payments, as there are fewer intermediaries and all transactions are simplified and transparent reducing billing errors and diagnosing quickly when and why happen.
SmartContracts Allow for Near Automated Agreements: Smart Contract allow the settings, triggers and execution of pre-planned supply orders and transportation services under conditions set out in pre-set agreements between the parties involved. For example, when a product is above a quantity in stock, or an order has just been closed with a supplier or customer.
Reduction of the Tail Wave Effect: end customers, have truthful and reliable information of what is happening in real time, without depending on providers or third parties. So, users throughout the supply chain have real control over the course of operations and able to foresee and address any disruption or compromise of the agreed service.
Passenger Transport
Enhanced Transparency and Cooperation: BlockChain allows a smooth and efficient integration of all services and an increase in transparency between the different parties involved. The agents involved in the entire transport chain including users, have total control over the achievement of the planned travel and visibility to the course of operations in real time, with truthful and reliable information about everything that happens, which allows to anticipate events or causes that may compromise the service offered and / or received.
Administrative and Operational Efficiency: as discussed BlockChain facilitates access to all information and documentation flow in real time making accessible and shareable to all parties so providing minimizing errors throughout the involved processes. Also in a similar way to Freight Transport errors, and bad practices can be easily detected and lack of quality becomes transparent to the customer and to the provider, and can be addressed more easily.
Disintermediation and Open Market Possibilities; BlockChain can help create an open, decentralized, multimodal and multi-vendor mobility market. The visibility an 100% reliability of information may act as a confidence builder between the different actors, improving collaboration even among authorities and opening door to new payment systems more accurate and secure and a global payment ecosystem with fewer intermediaries
Opportunity for Collaborative Economy Business Models: this technology and its inherent trust building effects has the clear potential to support and provide the business capabilities for the rise of integrated service among different agents acting as a network (collaborative economy).
Sources: CETMO and “Impacte de les KETs en la digitalització dels diferents àmbits del transport”, CENIT-CINESI – December 2020
With the support of:

Contact
Av. de Josep Tarradellas, 40, entresol
08029 Barcelona
Tel: 00 34 93 430 52 35
