Artificial Intelligence (A.I.) is the base of this ongoing 4th Industrial Revolution, along with Robotics and the Internet of Things. Since its inception, AI has been surrounded by hype, and has become part of the common language, therefore it requires some clarification about what in reality is and its evolution and its growing capabilities and impact.
A.I. DEFINITION
Intelligence and Artificial Intelligence
Intelligence can be roughly defined as learning, understanding, and using the knowledge learned to achieve goals. So artificial intelligence can be initially, simply defined as intelligence exhibited by machines.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that builds programs and machines that can creatively solve problems and are able to perform complex tasks. They do so by automatically combing and analyzing large amounts of observational data applying algorithms designed to find patterns.
AI and Machine Learning
Besides the proven capability of processing enormous data sets, AI is characterized by making possible for machines to learn from experience and adjust to new inputs. Machine Learning is achieved by applying iteratively complex mathematical calculations addressed to recognize patterns. AI adapts through progressive learning algorithms and finds structure and regularities in data so that the algorithms acquire a skill: The algorithm becomes a classifier or a predictor.
To do so iteration on large sets of data is essential, because when new data is provided the AI System applies what has already learned from previous computations, iterates the computation on new data and produces more reliable, results and decisions each time.
IA System learns only from the data provided. That means that any inaccuracies and obsolescence in the data set will be reflected in the results, therefore any additional layers of prediction or analysis need to be added separately.
As a result, most of today’s AI systems are trained to be limited to do a clearly defined task. These AI Systems are highly specialized: The AI System that detects for example insurance fraud, cannot identify identities on pictures of faces, even more, the system that can detect insurance fraud cannot detect tax fraud.
A.I. EVOLUTION
AI concept has been surrounded by hype since the concept was created along with the first neuronal mathematical models where created in late 1950s. Despite significant scientific advances, it was only in the 1990s that all the hype started to be justified. In the 1990s, Machine Learning became really functional and was quickly refined, leading to the massive adoption and use by industry and services by the end of the 90s.
Machine Learning and Integration
The improvement of AI accelerated during 2000s-2010s, further developing Machine Learning. However, it is only after 2010 that AI learning capacity has accelerated exponentially and expanded into a broad range of functions and tasks by integrating other new technologies.
Distributed Cloud Computing provides the massive computing power necessary to train algorithms and more complex models, sensors of Internet of Things and BigData generate and supply massive amounts of data that are necessary to train AI algorithms.
A good example of the advancing of AI by integrating new technologies are Autonomous vehicles that take advantage of innovations in sensors, mapping, machine vision, navigation algorithms, satellite technology, and robotics all brought together. Though impressive, AI being developed based on Machine Learning remain limited to solve specific problems and cannot tackle general problems in much the same way that humans do.
Learning Refinement Techniques
The learning is further improved applying innovative Data Training methods for a system to learn the relationships of a set of given inputs to a given output, this is used for example to recognize objects within an image or detect objects and describe their content. There is also the field of Reinforcement Learning to train AI System to learn from trial and error, by giving the AI System virtual rewards and punishments through a scoring system.
Presently there is a justified excitement over the exponential refinement and capability growth on Machine Learning by applying these new learning techniques. Additionally, and more importantly there is also the emerge of a new, more advanced field in AI known as Deep Learning.
A.I. NEW DEEP LEARNING
Deep Learning is the next level of machine learning, it is based on the addition of Neural Networks to the AI System, that simulate interconnected biological neurons and that model the way that neurons interact in a brain. This new neural-network provided Systems apply innovative learning techniques, which have already enormously improved them to classify, recognize, detect and describe the surrounding environment, in short providing AI Systems with something close to the capacity of understanding. Limitations remain, AI still faces many practical challenges, though new techniques are emerging to address them.
Deep Learning Integration Enablement
Besides radical improvements in algorithms, Neural networks and programming learning approaches, it is again the integration with other technical improvements that allow new efficiency and functions to AI Deep Learning Enabled machines.
Big Data plus Internet Data Streaming provide ever increasing amounts data from Internet of Things and its sensors and also from social media textual data from, plus human notes and transcripts, and with more data more neural networks can be build and more neural layers can be trained.
Cloud Computing Capacity Growth of to support deep algorithms training. Deep Learning allows State-of-the-art AI to achieve incredible accuracy which was previously impossible, for example our interactions with Google Search or Alexa are based on Deep Learning, and they become more accurate the more we use them. With Deep Learning, the algorithms are self-learning. BigData has become more important than ever, the more data the better the Deep Learning and the accuracy and complexity of tasks conducted by the AI System. More data, more competitive advantage.
A.I. GENERALIZED USE AND EFFECTS
AI is allowing and automating analysis no possible before with impacts on all business and administration departments, also allows sets of complex tasks and functions to be conducted fully autonomously or semi-autonomously by AI enabled automation and robotics machines. Additionally, AI is at the core of unmanned vehicles and drones.
By 2030, Artificial Intelligence are estimated to add $15.7 trillion to the global GDP, with $6.6 trillion projected to be from increased productivity and $9.1 trillion from consumption (1). Businesses are aware of it, already in 2017 an estimated 20% of firms worldwide were using AI at some level and another 40% were experimenting how to deploy it (2). The diagram below illustrates the broad range of technological maturity of AI and its use in a broad range of functions (3):
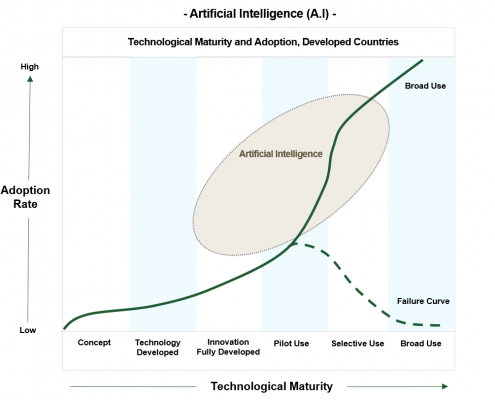
CETMO Analysis, adapted from McKinsey & Company (3)
For business, the largest impacts are and will be in logistics and supply chain sector followed by manufacturing, not only in production and operations but also in marketing and sales through personalization and market segment and niche adjusted services and products.
For administrations AI’s supported enhanced and faster human decision-making and planning has an undeniable potential to improve social outcomes and lo leverage scarce resources.
As in many other of the KETTLs presented, there is an ongoing and intense debate among experts about if AI will consolidate existing business competitive advantages or will level the playfield advantages, in any case the conclusion is that to avoid serious disadvantages business should be exploring its use and deployment.
Additionally, there is a similarly intense and in concluded debate about the broader social impact of AI and in particular the net impact, and how to improve it, on the labor force and in Country Disparity. This, essential issue deserves and requires a separate and dedicated analysis.
References:
- Brookings Institute. Africa Growth Initiative. Travaly and Muvunyi, the future is intelligent: Harnessing the potential of artificial intelligence in Africa, 2020. link
- Bughin, Chul, McCarthy, How to make A.I. work for your Business, 2017
- McKinsey & Company. Ashutosh, Hastings, Murnane, Neuhaus, Automation in Logistics: Big Opportunity, Bigger Uncertainty, 2019. link
Artificial Intelligence
Fast advances in IA learning techniques, new Neuronal Networks that allow Deep Learning, falling costs, and integration with other KETTLS like Cloud Computing, Internet of Things and Robotics allows AI growing capabilities, technological mature and increasing general adoption. Some specific effects are:
A.I. Effects on Freight Transport
Decision Making Support: Artificial Intelligence, particularly if applied to Big Data Analytics enables advanced business intelligence tools, Advanced predictive modelling and generation of indicators and dashboards among others, which will show an accurate picture of the company and situation thus allowing to make better and less risky decisions.
Semi-Autonomous Security and Supervision of infrastructures and terminals increasing the control capabilities with sensors of temperature, humidity, and other environment control metrics thus allowing to control large spaces at a lower cost.
Price Setting Optimization: with greater adjustment to costs and commercial strategy of each of the network routes that allowing it to be optimized for each case and expanding the possibilities of yield management.
A.I. Effects on Passenger Transport
Decision Making Support: in the same way that affects Freight Transport and other industries, Artificial Intelligence will enable the use of advanced and more reliable predictive models, making planning easier.
In the most forward scenario IA based modeling and other IA advanced tools may even replace pre-planning with an instant, continuous, and automatic adjustment of the service to respond to evolving needs, saving time and gaining in quality.
Safety Improvement and Maintenance Cost Reduction: IA allows for predictive maintenance of infrastructure and rolling stock rolling stock like Infrastructure MRO (Maintenance, Repair & Overhaul), rolling stock MRO, plus energy consumption optimization.
Artificial Intelligence and Passengers:: IA along with facial recognition and other biometric applications will optimize processes that require identity check such as the check-in of luggage, documentation and border control and should allow for faster, less error-prone traveler experience and administrative procedures.
Cloud computing
Cloud computing provides enormous computational power on-demand, without fixed costs and access to third-party on-the-cloud applications,
This technology is the base and enabler of most of the KETTLs here being analyzed.
- CC provides third party applications and access to AI to a broader range of agents.
- CC is the necessary base for BigData, to collect, apply computer power and analyze enormous data-sets.
- AI, in itself is based on learning, and its only by repetitively analyzing huge and changing datasets provided by BigData, which in turn is based on CC:
- Also it’s at the base of the IoT allowing sensor data collection, integration, analysis and also sending back to the devices how to act.
- Plays a similar role in Unmanned vehicles and advanced robotization.
For this reason, more than a KETTLE, Cloud Computing is the predecessor and base of these technologies.
CC is already a Near-Mature technology with massive range of evolving functions. It’s been broadly adapted, with a present increasing in demand by developing nations and mid-size companies and administration agencies. The technological maturity plus its generalized adoption makes the main infrastructure of the Key Enabling Technologies, more than a KETTL itself.
CC Effects on Freight Transport
Ubiquitous and Cost Efficient Access to Data and digital services of added value like software / hardware tools that require large investments in computing capacity or storage on servers. Business Capacities now paid for usage and not requiring initial investment.
Software and Technology Improvement: with the proliferation of new digital tools, no significant upfront investment is required to access them becoming new business capabilities.
CC Effects on Passenger Transport
Cost Efficient Access to New Capabilities: that require great computing power. Consolidation of widespread use of digital tools by universalizing access to them by operators.
Change Operators-Suppliers Business Relationships due to new ways they access the capabilities (new services such as connection to remote servers, etc.).
Data Access by Users: as it facilitates at no significant incremental cost access to the necessary data by users.
Big Data
BigData Effects on Freight Transport
Improved Planning: searching, retrieving and processing large volumes of data in real time (such as costs, constraints, limitations, asset location, etc.) helps to improve operations forecasts and support tools (such as freight market, fuel purchase, weather forecast, travel time, etc.).
More Accurate Asset Lifetime Analysis: lifetime analysis and preventive maintenance of machinery and other movable assets is more accurate reducing fix costs and improving the Balance Sheet.
Network optimization: data analysis leads to optimization of routes and in general reduction of operating costs and future investments.
Operations Fine-Tuning: information support and measurement of operations allow to establish realistic criteria adjusted to the real circumstances and to improve the design and control of operations.
New Skills Required: as there is a need to incorporate new technical profiles in fields related to mathematical computing, Data Science and Operations Research.
BigData Effects on Passenger Transport
Improved Planning and Fleet management: similarly, to Freight Transportation Big Data Analytics allows to improve operations, forecasts and support tools. Additionally, allows to optimize decision making by providing more and better indicators, and to develop new products and services from a new perspective more adapted to the real needs of travelers. This allows the optimization vehicles, routes and costs (even instantly or with future simulations).
More Accurate Asset Lifetime Analysis: same as Freight Transport.
Trends, Micro-Segmentation and Improved Customer Service: Big Data Analytics allows to forecast megatrends, changes in customer behavior and micro-segmentation. Also allows to provide integrated customized information to the customer while purchasing and travelling.
New Skills Required: similar as Freight Transport.
Sources: CETMO and “Impacte de les KETs en la digitalització dels diferents àmbits del transport”, CENIT-CINESI – December 2020
With the support of:

Contact
Av. de Josep Tarradellas, 40, entresol
08029 Barcelona
Tel: 00 34 93 430 52 35
